display property defines how a certain html element should be displayed.
Because of poor browser support, only three display property values ever gets used:
- inline (default)
- block
- none
The inline value allows you to define an element to behave as though it were an inline element (like a span or an anchor tag).
Conversely, the block value lets you force block-level behavior (like a div or a paragraph).
And "display: none" simply causes an element to not display at all.
Eg: To hide a paragraph
<p style="display: none;">hello world</p>
Eg2: inline
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
span#mySpan
{
background-color:red;
display:inline;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>A span element.</span>
<span id="mySpan">Another span element.</span>
<span>Another span element.</span>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:

Eg3: block
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
span#mySpan
{
background-color:red;
display:block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>A span element.</span>
<span id="mySpan">Another span element.</span>
<span>Another span element.</span>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:

Eg4: list-item
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
span {
margin-left: 10px;
}
span#mySpan
{
background-color:red;
display:list-item;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>A span element.</span>
<span id="mySpan">Another span element.</span>
<span>Another span element.</span>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:

Display values:
inline inline makes the element generate one or more inline boxes.
block block makes the element generate a block box.
none A value of none makes the element generate no box at all.
Descendant boxes cannot generate boxes either, even if their display property is
set to something other than none.
inline-block inline-block makes the element generate a block box that’s laid out as if it were an inline box.
inline-table inline-table makes the element behave like a table that’s laid out as if it were an inline box.
list-item list-item makes the element generate a principal block box and a list-item inline box for the list marker.
run-in A value of run-in makes the element generate either a block box or an inline box,
depending on the context.
If the run-in box doesn’t contain a block box, and is followed by a sibling block box (except a table caption)
in the normal flow that isn’t, and doesn’t contain, a run-in box, the run-in box becomes the first inline box of
the sibling block box. Otherwise, the run-in box becomes a block box.
table table makes the element behave like a table.
table-caption table-caption makes the element behave like a table caption.
table-cell table-cell makes the element behave like a table cell.
table-column table-column makes the element behave like a table column.
table-column-group table-column-group makes the element behave like a table column group.
table-footer-group table-footer-group makes the element behave like a table footer row group.
table-header-group table-header-group makes the element behave like a table header row group.
table-row table-row makes the element behave like a table row.
table-row-group table-row-group makes the element behave like a table body row group.
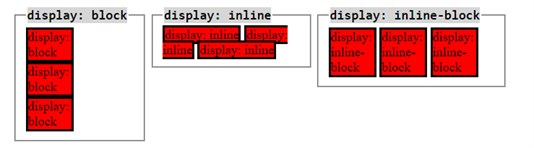
Differences between 'display: block', 'display: inline' and 'display: inline-block':
Block element:
1. does not tolerate any html elements next to it.
2. forces a line break after the block element. A block element has some whitespace above and below it.
Inline element:
1. has no line break before or after it.
2. allows other elements to sit to their left and right, ie: it tolerates html elements next to it.
For more information, see here.
3. respects left and right margins and padding, but NOT top and bottom.
4. cannot have a width and height set.
Inline-block element:
'inline-block' is a hybrid that creates a rectangular region (a block), and doesn't create any new lines (hence 'in line'):
1. allows other elements to sit to their left and right. That is, it is placed as an inline element (on the same line as adjacent content), but it behaves as a block element.
2. respects top and bottom margins and padding.
3. respects height and width.
Example of block, inline and inline-block elements:
Eg:
Compare with css visibility position property here.
For more information on difference between div and span tags, see here.