Css positioning properties (like position, z-index etc...) allow you to position an element. It can also place an element behind another, and specify what should happen when an element's content is too big.
Elements can be positioned using the top, bottom, left, and right properties. However, these properties will not work unless the position property is set first.
They also work differently depending on the positioning method.
position property:
position property specifies the type of positioning method used for an element (static, relative, absolute or fixed).
There are 4 different positioning methods:
1. Static Positioning
2. Fixed Positioning
3. Relative Positioning
4. Absolute Positioning
1. Static positioning:
Html elements are positioned static by default.
A static positioned element is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page.
Static positioned elements are not affected by the top, bottom, left, and right properties.
2. Fixed positioning:
An element with fixed position is positioned relative to the browser window.
It will not move even if the window is scrolled:
Eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p.pos_fixed {
position:fixed;
top:30px;
right:5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="pos_fixed">Some more text</p>
<p><b>Note:</b> IE7 and IE8 supports the fixed value only if a !DOCTYPE is specified.</p>
<p>gibberish text</p>
<p>gibberish text</p>
<p>gibberish text</p>
<p>gibberish text</p>
<p>gibberish text</p>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:

Eg2: fixed header:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
body {
margin:0px;
background:lightgrey;
}
.header_content {
width:100%;
position:fixed;
top:0px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
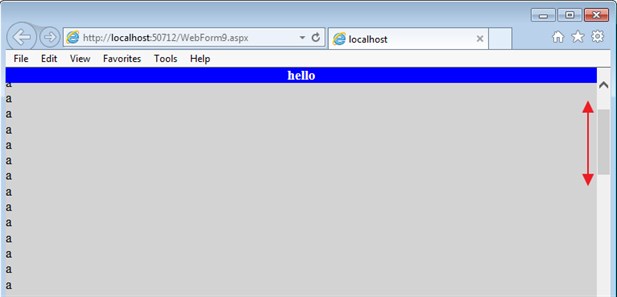
<div class="header_content" style="background-color:blue;color:white;font-weight:bold;text-align:center">
hello
</div>
a<br />
a<br />
a<br />
... etc...
</body>
</html>
Outputs:
For more information, see here.
3. Relative positioning:
A relative positioned element is positioned relative to its normal position.
Eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h2.pos_left {
position:relative;
left:-20px;
}
h2.pos_right {
position:relative;
left:20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>heading with no position</h2>
<h2 class="pos_left">heading is moved left according to its normal position</h2>
<h2 class="pos_right">heading is moved right according to its normal position</h2>
<p>Relative positioning moves an element RELATIVE to its original position.</p>
<p>The style "left:-20px" subtracts 20 pixels from the element's original left position.</p>
<p>The style "left:20px" adds 20 pixels to the element's original left position.</p>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:

Eg2: The content of relatively positioned elements can be moved and overlap other elements, but the reserved space for the element is still preserved in the normal flow.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h2.pos_top {
position:relative;
top:-40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>heading with no position</h2>
<h2 class="pos_top">heading overlap</h2>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:
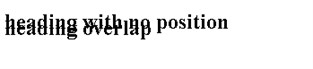
4. Absolute positioning:
An absolute position element is positioned relative to the first parent element that has a position other than static.
If no such element is found, the containing block is <html>:
Eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h2 {
position:absolute;
left:100px;
top:150px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>heading with an absolute position</h2>
<p>With absolute positioning, an element can be placed anywhere on a page. The heading below is placed 100px from the left of the page and 150px from the top of the page.</p>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:

z-index property: overlapping elements:
When elements are positioned outside the normal flow, they can overlap other elements.
The z-index property specifies the stack order of an element (which element should be placed in front of, or behind, the others).
An element can have a positive or negative stack order.
An element with greater stack order is always in front of an element with a lower stack order.
Note: If two positioned elements overlap, without a z-index specified, the element positioned last in the html code will be shown on top.
Eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
img {
position:absolute;
left:0px;
top:0px;
z-index:-1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<img src="happyface.png" width="100" height="140" />
<p>Because the image has a z-index of -1, it will be placed behind the text.</p>
</body>
</html>
Outputs:
