Type selectors:
Type selectors will select any html element on a page that matches the selector, regardless of their position in the document tree.
Eg: this rule will select any <em> element on the page, and color it blue.
em { color: blue; }
Css combinators:
There are four different combinators in css:
1. descendant selector (space)
2. child selector (>)
3. adjacent sibling selector (+)
4. general sibling selector (~)
1. Descendant selectors (space):
Descendant selectors are used to select elements that are descendants of another element in the document tree.
Eg: to target a specific <em> element on the page, use:
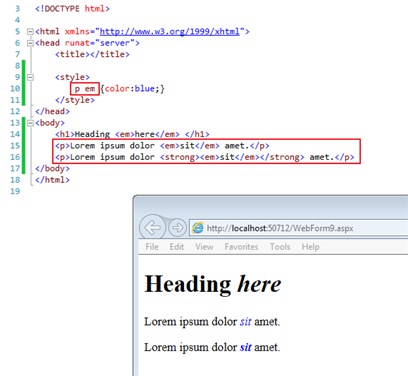
<style>
p em {color:blue;}
</style>
<body>
<h1>Heading <em>here</em> </h1>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor <em>sit</em> amet.</p>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor <strong><em>sit</em></strong> amet.</p>
</body>
Outputs:
Eg2: You can also jump levels in the document tree structure to select descendants.
Using the following rule you can isolate any <em> element inside a <ul> element, without having to describe the <li> element. If this rule is applied, any <em> element within a <ul> element will be colored blue. However, the <em> element within the <p> will not be colored blue:
ul em {color:blue;}
<body>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor <em>sit</em> amet.</p>
<ul>
<li>item 1</li>
<li>item 2</li>
<li><em>item 3</em></li>
</ul>
</body>
2. Child selectors (>):
A child selector is used to select an element that is a direct child of another element (parent). Child selectors will not select all descendants, only direct children.
Eg: to target an <em> that is a direct child of a <div>, but not other <em> elements that are descendants of the <div>
Using the following rule you can target any <em> element that is a child of the <div>. Other <em> elements that are descendants but not direct children of the <div> will not be targeted:
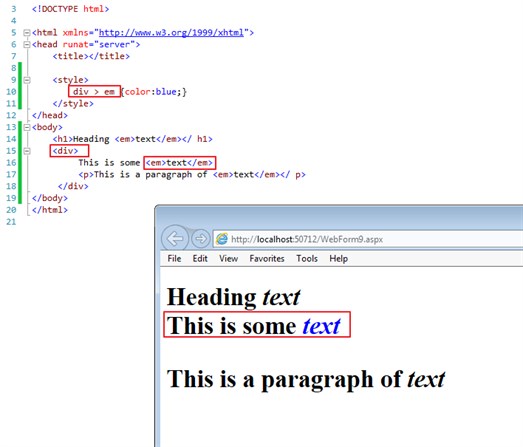
div > em {color:blue;}
or:
div>em {color:blue;}
<body>
<h1>Heading <em>text</em></ h1>
<div>
This is some <em>text</em>
<p>This is a paragraph of <em>text</em></ p>
</div>
</body>
Outputs:
Eg2: child of child
#structure1 > .tile_container > .tile2.on
{
background-color: #FFD3D3;
}
Universal selectors:
Universal selectors are used to select any element.
Eg: the rule below will color all html elements on a page blue - regardless of their position in the document tree
* {color:blue;}
3. Adjacent sibling selectors (+):
Adjacent sibling selectors will select the sibling immediately following an element.
Eg: to target an <h3> element, but only <h3> elements that immediately follow an <h2> element:
Use the following rule, you can target any <h3> that follows an <h2>:
h2 + h3 {margin:-1em;}
<body>
<h2>Heading 2 <em>text</em></ h2>
<h3>Heading 3 text</h3>
<p>This is <em>text</em> and more <strong>text</strong></ p>
</body>
Note: this example is a commonly used in the real-world as there is often too much space between <h2> and <h3> elements when they appear immediately after each other.
Eg2: adjacent sibling selectors also work for inline elements such as <em> and <strong>
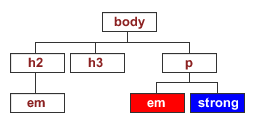
em + strong {color:blue;}
4. General sibling selector (~):
The general sibling selector selects all elements that are next siblings of a specified element.
Eg: following example selects all <p> elements that are next siblings of <div> elements:
div ~ p {
background-color: yellow;
}
Attribute selectors:
Attribute selectors are used to select elements based on their attributes or attribute value.
Attribute: All html elements can have associated properties, called attributes. These attributes generally have values. Any number of attribute/value pairs can be used in an element's tag - as long as they are separated by spaces. They may appear in any order.
Eg:
<h1 id="section1">
<img src="small.gif" width="100" height="100">
<img title="mainimage" alt="main image">
<a href="foo.htm">
<p class="maintext">
<form style="padding: 10px">
Use following rule to select any image on an html page that is called 'small.gif':
img[src="small.gif"] { border: 1px solid #000; }
There are four types of attribute selectors:
1. to select based on attribute:
Eg: below will select an element (in this case 'img') with the relevant attribute:
img[title] { border: 1px solid #000; }
img[width] { border: 1px solid #000; }
2. to select based on value:
Eg: select any image whose attribute, in this case 'src', has a value of 'small.gif':
img[src="small.gif"] { border: 1px solid #000; }
Eg2: to select based on input type number:
input[type="number"]
{
text-align:right;
}
3. to select space separated instances of a value:
Eg: will select any image whose attribute (in this case 'alt') contains a space separated list of words, in this case any 'alt' that includes the word 'small':
img[alt~="small"] { border: 1px solid #000; }
4. to select hyphen separated instances of a value:
Eg: will select any image whose attribute, in this case 'title', has a hyphen separated list, in this case any title that includes 'small-':
img[title|="small"] { border: 1px solid #000; }
To select by id, see here.
To select by class, see here.
And here.