Use Windows Taskmanager to track memory usage.
To open Taskmanager:
1. Keyboard, Ctrl + shift + Esc
2. Right click on the taskbar and click "task manager"
3. Hold Ctrl, Alt, and Delete for 1 second, then release
You will find the program at:
C:\WINDOWS\system32\taskmgr.exe
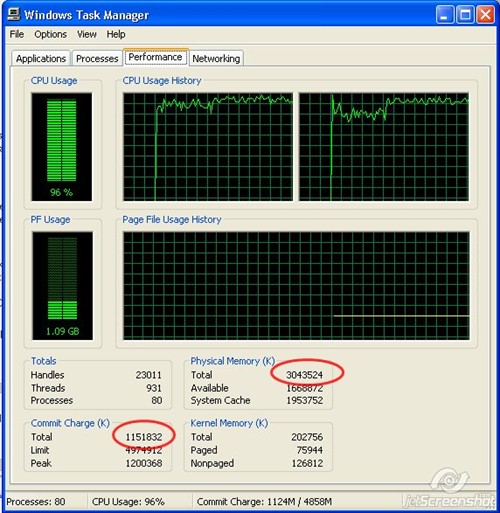
To see how much memory is in use, open Task Manager and click the Performance tab.
You should look at only two values here for the most part.
Under the Physical Memory heading, there is roughly 3 gigs of physical ram installed based on the above example.
If your system uses a shared ram video adapter you may discover that you have less physical ram than you thought.
The total under Commit Charge heading indicates how much ram is actually in use by programs and processes.
If the number here is bigger than the amount of physical ram, it means your system has been forced to swap data to disk, and that’s the cause of the current performance problem.
To view how much ram is in use by each program or process, click the Processes tab and then click the Mem Usage heading to sort the list in order.
You can use this information to decide which programs to close so that you can return to normal performance.
Note: it’s perfectly fine for a process to use a large amount of ram if you’ve got the physical ram to spare. Don’t start closing programs that use large amounts of ram.
If you find yourself regularly using more memory than you have physical ram, ie: if the Total Commit Charge is consistently more than Total Physical ram, it’s time to order a memory upgrade.