How to Backup the Windows Registry:
Steps:
1. Press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
2. In the left pane, click on Computer (the top of the tree).
3. Go to the File menu > click Export. Export Range: All
This creates a full .reg file that you can double-click later to restore everything if needed.
Eg:
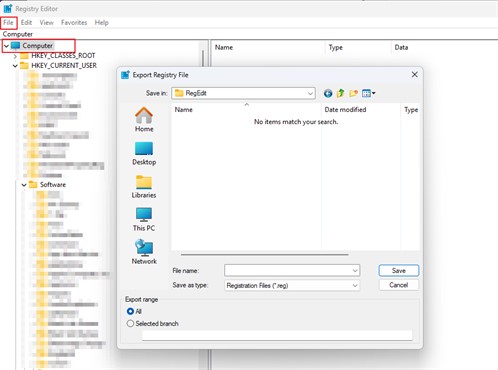
How to Restore Registry:
If a registry change breaks something:
Steps:
1. Locate your .reg backup file.
2. Double-click it and confirm "Yes" when asked to add it back into the registry.
3. Restart your computer to ensure the restored settings take effect.
Note: you can back up part of the registry, Eg: say only the SQL Server – related keys instead of the whole registry if you wanted to.
Note2: ony a very recent registry backup shoud be used to to restore a pc registry to fix an issue; preferably from a backup made just before a new issue.
Restoring a backup after a long period, especially after a Windows update, can be risky because:
1. System Changes: windows updates modify the registry, adding new entries and removing outdated ones. Restoring an old backup could overwrite these changes, potentially causing instability.
2. Software Compatibility: if you've installed or updated programs since the backup, restoring an older registry could break functionality.
3. Driver & Security Updates: restoring an outdated registry might interfere with updated drivers or security patches.
If you need to undo a recent change, a registry backup is useful.
But for broader system issues, a System Restore Point or a full backup is often a safer choice.
No Restart Needed:
Most registry changes take effect immediately or the next time the affected app/service starts, so no pc reboot is needed.
Eg: changing a registry setting for SQL Server services > restarting the SQL Server service is usually enough.
Eg2: editing user preferences or configuration keys.
Restart or Service Restart Needed:
You do need to restart (or at least restart a service) when:
The registry change affects a Windows service that is already running (Eg: SQL Server or SQL Agent).
You delete registry entries tied to installed programs or drivers.
You make changes under:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\
Anything that affects system startup or low-level drivers.